Some people believe cataracts to be a form of color blindness, but they are not. Cataracts are a clouding that develops on the crystalline lens of the eye, and the effect is to cloud vision. Color vibrancy is definitely reduced with cataracts, hence the common misconception that it is a form of color blindness. However along with vibrancy, clarity is also reduced in line with symptoms of short sightedness etc. Rather than a genetic mutation of a gene or a defect in the shape or structure of the eye, cataracts are instead a disease that disables correct vision by obscuring incoming light waves.
Cataract Symptoms
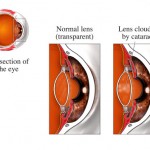
As a cataract strengthens, vision quality will be compromised in a few ways. A person will lose sensitivity to color contrast causing contours, shadows, and colors in general to become less vivid. A cataract scatters light as it enters the eye, causing a veiling glare over someone’s vision. Early signs of cataracts are typically seeing a halo around bright lights at night – for example street lights when driving. The degradation of vision as a result of cataracts quickly becomes quite prominent, but if you are unsure you should undertake a contrast sensitivity test, and if a loss in sensitivity is detected – visit an eye specialist as early detection is always favourable.
Cataracts Causes
Cataracts develop as a result of various reasons, and can be partial, complete, progressive or stationary, and hard or soft. Common causes include:
- Long-term UV exposure
- Radiation exposure
- Side-effects of old age, trauma, hypertension, and diseases such as diabetes
- Drug usage, known drugs include Corticosteroids, Ezetimibe, and Seroquel
- Family history
Cataracts are typically associated with old age however eye injuries and trauma, a genetic family history and drug usage can often cause early development of cataracts. Studies have found that some people in professions including piloting aircraft, and glassblowing have a higher occurrence rate of cataracts. Allergic reactions have also been identified as a catalyst for the progression of cataracts – especially for children with cataracts.
Cataract Types
Anterior or Nuclear Cataracts are the most common, as they are related to aging, however there are a number of other types that affect all ages. Some babies are born with congenital cataracts, they may be present at birth or develop during childhood but do not always affect the child’s vision. Cortical cataracts are typically found in patients with diabetes; they begin at the outer rim of the lens and gradually work toward the core. Sub-scapular cataracts progress the most rapidly of all types, affecting the back of the lens causing glare and blurriness and are most often the result of steroid use, but also from diabetes or found in patients who suffer extreme nearsightedness.
Preventing Cataracts
There is no scientifically proven method to prevent cataracts. However there are logical ways to avoid cataracts that form as a result of your lifestyle. If you spend a lot of time in the sun, UV filtering eye-ware can greatly reduce the risk of forming cataracts as a result of UV overexposure. Likewise making a healthy choice to avoid taking steroids for anything other than to aid other medical issues will greatly reduce the risk of developing sub-scapular cataracts. Vitamin A is well known to be required for healthy eyesight, maintaining the recommended intake of Vitamin A as well as C and E can theoretically be helpful, however it has been shown that taking an excess of these vitamins has no further positive effect.
Cataract Surgery – Cure
The only solution for cataract sufferers is cataract surgery. To be removed by surgery the cataract must generally first reach a suitable level of development. The standard method of removal is to make an incision into the capsule of the cloudy lens in order to surgically remove it. Eye surgery to remove cataracts comes in two flavours: Extracapsular cataract extraction, and Intracapsular cataract extraction.
- Extracapsular eye surgery involves removing the lens but leaving the majority of the lens capsule intact. Sometimes high frequency sound waves are used to break up the lens before extraction
- Intracapsular eye surgery involves removing the entire lens of the eye however it is rarely performed in modern practice.
Regardless of the method, once the diseased lens is removed, a permanent synthetic lens replaces it. The surgery is usually performed using local anaesthetic and a patient will be able to go home on the same day. Modern improvements have also offered patients the choice of multi focal plastic lenses that can reduce the reliance of the patient on glasses. Patients also suffer little to no discomfort during or after the surgery, and the success rate of restoring useful vision is in excess of 90%. Laser and Lasik technologies are currently being used with high success to correct short and long sightedness as well as other eye dysfunctionality however laser eye surgery is not yet being used for cataract removal.